Many-to-Many Relationship in Database
In relational database design, a many-to-many relationship is a type of association where multiple records in one table are related to multiple records in another table. Many-to-many relationships are commonly encountered in real-world applications, such as users belonging to multiple groups or products associated with multiple categories.
In relational database design, a many-to-many relationship is a type of association where multiple records in one table are related to multiple records in another table. Many-to-many relationships are commonly encountered in real-world applications, such as users belonging to multiple groups or products associated with multiple categories.
Many-to-Many Relationship
A many-to-many relationship exists when:
- Each record in Table A can be associated with multiple records in Table B.
- Each record in Table B can be associated with multiple records in Table A.
In relational databases, many-to-many relationships are handled by introducing a junction table (also called an associative or linking table) that bridges the two tables.
Example Use Cases
- Authors and Books: An author can write multiple books, and a book can be authored by multiple authors.
- Products and Categories: A product can belong to multiple categories, and each category can include multiple products.
ER Diagram
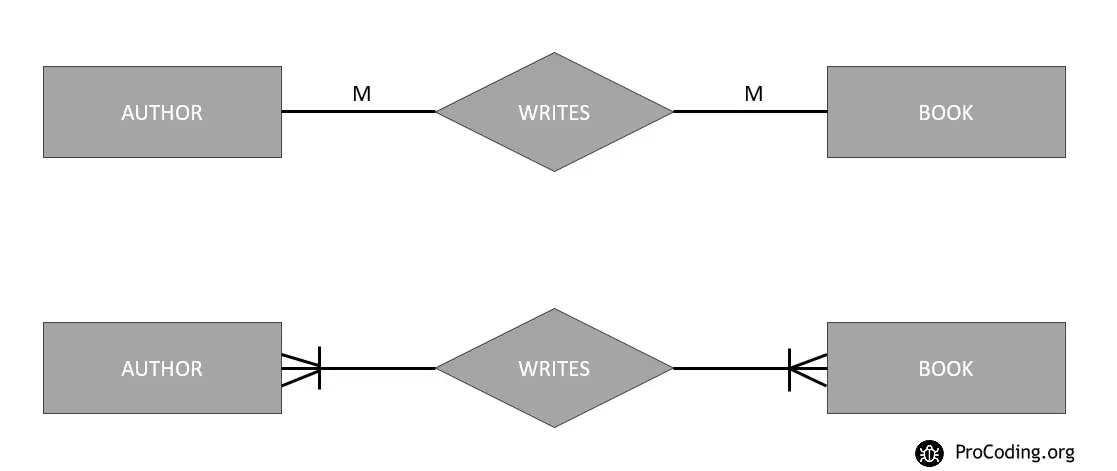
Let's drop this diagram into the tables -
author_id will be the primary key in the author table and book_id will be the primary in the book table.
author_id and book_id will be marked as composite primary keys in the writes (intermediate) table so that no duplicate entries will be added.
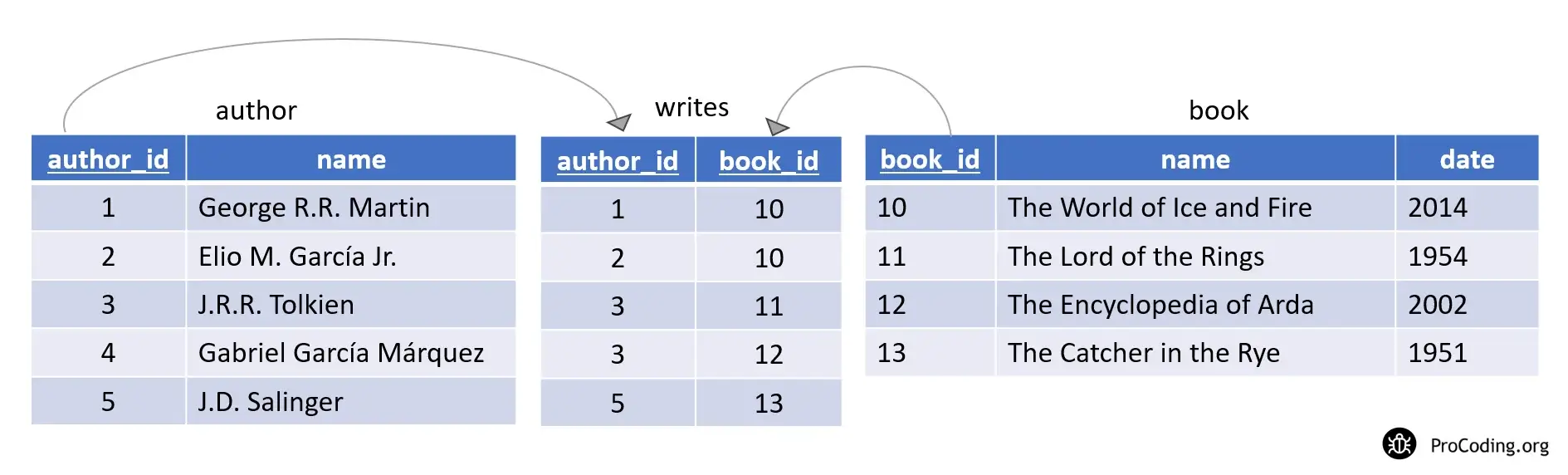
Here, notice how we are maintaining the information -
- The World of Ice and Fire is written by two writers - George R.R. Martin and Elio M. García Jr.
- J.R.R. Tolkien has written two books - The Lord of the Rings and The Encyclopedia of Arda
SQL Query
Let's create the author and book table first -
CREATE TABLE author (
author_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE book (
book_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
date DATE
);
Now let's create the junction table to establish the relation between the tables
CREATE TABLE writes (
author_id INT,
book_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY (author_id) REFERENCES author(author_id),
FOREIGN KEY (book_id) REFERENCES book(book_id),
PRIMARY KEY (author_id, author_id)
);