Compare structure and data of two binary trees
Write a program to compare the structure data of two binary trees and if they are identical then return true otherwise false by checking each node in the given binary trees.
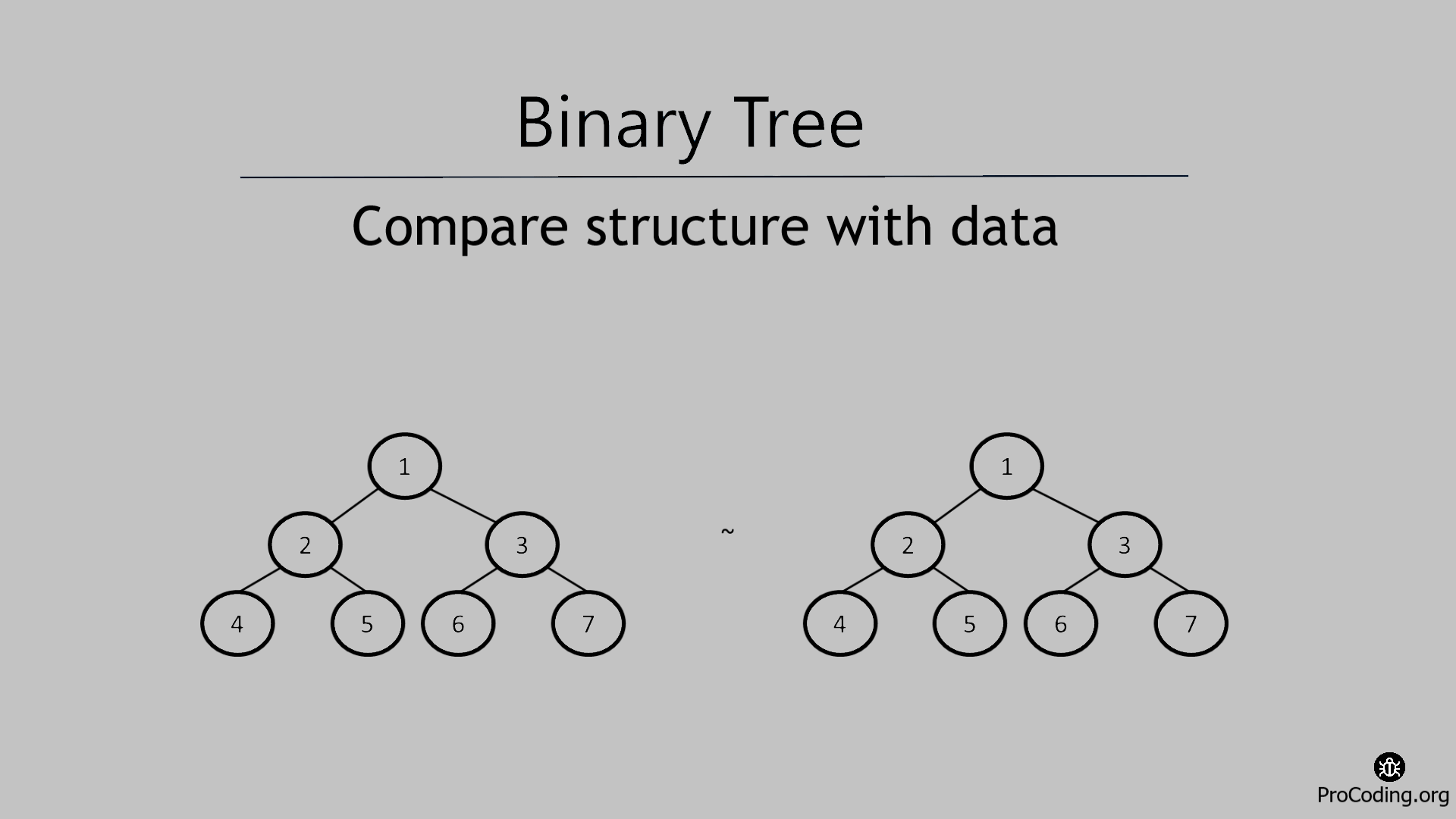
In this problem, we will try to compare the structure and data of two binary trees and if the structure and data of both the binary trees are same then return true otherwise false.
So we have to compare both, structure and data of the given trees and return the result accordingly to check if the trees are identical or not.
Example -
Input:
1 5
/ \ / \
2 3 4 6
/ / \ / / \
4 6 7 3 2 1
Output: False
Input:
1 5
/ \ / \
2 3 2 3
/ / \ / / \
4 6 7 4 6 7
Output: True
Input:
1 5
/ \ / \
2 3 4 6
/ / \ / \
4 6 7 2 1
Output: False
We can solve this problem in two ways-
Recursive solution
To solve this problem recursively, traverse both the trees simultaneously and check if both are identical or not by comparing the structure and data as well by checking the presence of child/children of the trees with data.
Algorithm
Compare_Structure(root1, root2)
1. if root1 is null AND root2 is null then
2. return true
3. if root1 is null OR root2 is null then
4. return false
5. if root1.data == root2.data then
6. return Compare_Structure(root1.left, root2.left) AND
Compare_Structure(root1.right, root2.right)
7. return false
Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.data = data
self.right = None
def compare_structure(root1, root2):
if root1 is None and root2 is None:
return True
if root1 is None or root2 is None:
return False
if root1.data == root2.data:
return compare_structure(root1.left, root2.left) and compare_structure(root1.right, root2.right)
return False
root1 = Node(1)
root1.left = Node(2)
root1.right = Node(3)
root1.left.left = Node(4)
root1.left.right = Node(5)
root1.right.left = Node(6)
root1.right.right = Node(8)
root2 = Node(1)
root2.left = Node(2)
root2.right = Node(3)
root2.left.left = Node(4)
root2.left.right = Node(5)
root2.right.left = Node(6)
root2.right.right = Node(7)
print(compare_structure(root1, root2))
JavaScript
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.data = data;
this.right = null;
}
}
function compareStructure(root1, root2) {
if (root1 == null && root2 == null) return true;
if (root1 == null || root2 == null) return false;
if (root1.data == root2.data) {
return (
compareStructure(root1.left, root2.left) &&
compareStructure(root1.right, root2.right)
);
}
return false;
}
const root1 = new Node(1);
root1.left = new Node(2);
root1.right = new Node(3);
root1.left.left = new Node(4);
root1.left.right = new Node(5);
root1.right.left = new Node(6);
root1.right.right = new Node(8);
const root2 = new Node(1);
root2.left = new Node(2);
root2.right = new Node(3);
root2.left.left = new Node(4);
root2.left.right = new Node(5);
root2.right.left = new Node(6);
root2.right.right = new Node(7);
console.log(compareStructure(root1, root2));
Output
False
Iterative solution
For iterative solution, we have to traverse both the trees in level order simultaneously and use a helper function to compare both the nodes.
To handle nodes from two trees, store a pair of nodes in the queue and pass one by one the pair of nodes to the helper function.
Algorithm
Check(node1, node2)
1. if node1 is null AND node2 is null then
2. return true
3. if node1 is null OR node2 is null
4. return false
5. if node1.data != node.data then
6. return false
7. return true
Compare_Structure(root)
1. queue.enque(Array(root1, root2))
2. while queue is not empty
3. node = queue.dequeue()
4. root1 = node[0]
5. root2 = node[1]
6. if not Check(root1, root2) then
7. return false
8. if root1 is not null then
9. queue.enqueue(Array(root1.left, root2.left))
10. queue.enqueue(Array(root1.right, root2.right))
11. return true
Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.data = data
self.right = None
# helper function to check if nodes have the same structure and data
def check(p, q):
if not p and not q:
return True
if not q or not p:
return False
if p.data != q.data:
return False
return True
def compare_structure(root1, root2):
queue = [(root1, root2),]
while queue:
root1, root2 = queue.pop(0)
if not check(root1, root2):
return False
if root1:
queue.append((root1.left, root2.left))
queue.append((root1.right, root2.right))
return True
root1 = Node(1)
root1.left = Node(2)
root1.right = Node(3)
root1.left.left = Node(4)
root1.left.right = Node(5)
root1.right.left = Node(6)
root1.right.right = Node(8)
root2 = Node(1)
root2.left = Node(2)
root2.right = Node(3)
root2.left.left = Node(4)
root2.left.right = Node(5)
root2.right.left = Node(6)
root2.right.right = Node(7)
print(compare_structure(root1, root2))
JavaScript
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.data = data;
this.right = null;
}
}
// helper function to check if nodes have same structure and data
function check(p, q) {
if (!p && !q) return true;
if (!q || !p) return false;
if (p.data != q.data) return false;
return true;
}
function compareStructure(root1, root2) {
const queue = [[root1, root2]];
while (queue.length > 0) {
node = queue.shift();
root1 = node[0];
root2 = node[1];
if (!check(root1, root2)) {
return false;
}
if (root1) {
queue.push([root1.left, root2.left]);
queue.push([root1.right, root2.right]);
}
}
return true;
}
const root1 = new Node(1);
root1.left = new Node(2);
root1.right = new Node(3);
root1.left.left = new Node(4);
root1.left.right = new Node(5);
root1.right.left = new Node(6);
root1.right.right = new Node(8);
const root2 = new Node(1);
root2.left = new Node(2);
root2.right = new Node(3);
root2.left.left = new Node(4);
root2.left.right = new Node(5);
root2.right.left = new Node(6);
root2.right.right = new Node(7);
console.log(compareStructure(root1, root2));
Output
False
Time complexity: Assuming first binary tree has 'n' nodes and second binary tree has 'm' nodes then node count of the tree having less number of nodes will be considered for time complexity i.e., if n < m then time complexity will be O(n) otherwise it will be O(m).